 Brain hemorrhage is an extremely dangerous and life-threatening situation that occurs due the disruption of complex and dense vessel network and leaking of blood around or into the brain.
Brain hemorrhage is an extremely dangerous and life-threatening situation that occurs due the disruption of complex and dense vessel network and leaking of blood around or into the brain.
Patients with hypertension and diabetes, beware..
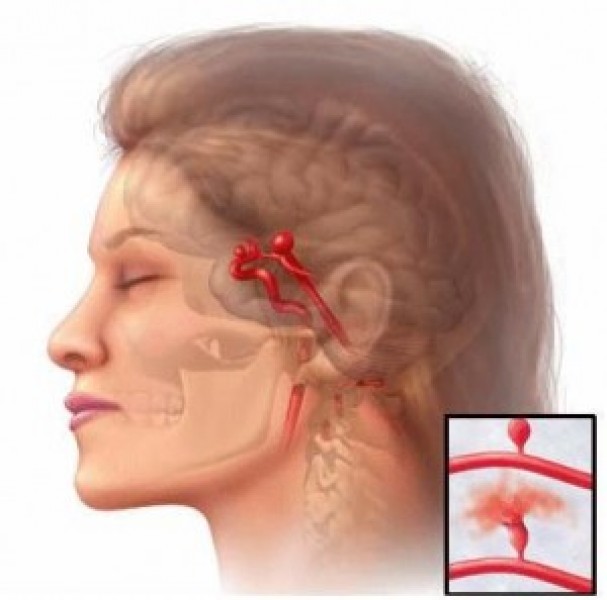
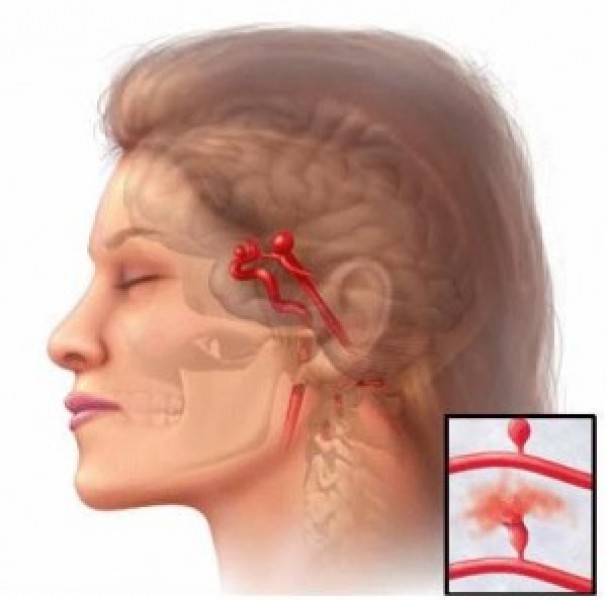
Brain hemorrhages are caused by ruptured vascular anomalies in the vessel network of the brain lie vessel balloons (aneurysms) or tangle of vessels (arteriovenous malformations) or sudden rupture of vessel walls due to the damage of hypertension or diabetes. Using high dose blood thinning medications, hardening of the arteries, and factors that cause this like smoking, alcohol and unhealthy diet are other factors that can result in these bleedings. Blows to the head can also be a reason. When these underlying causes are present, sudden sneezing, cough, to strain while defecating, sexual intercourse and heavy lifting can precipitate bleeding.
Types of bleeding …
Brain hemorrhages can be in form of subarachnoid hemorrhage (bleeding around the brain and into its indentations, usually caused by ruptured aneurysms), intraventricular hemorrhage (bleeding into big spaces within the brain, usually caused by vascular diseases) or intracerebral hemorrhage (bleeding within the brain tissue, usually caused by arteriovenous malformations, tumors or vascular diseases that involve vessel walls).
Treatment…
Treatment by entering the veins from groin and clogging the balloon is preferred in aneurysm bleedings. If this procedure is “inapplicable” in certain cases, open brain surgery is performed to clip and close the aneurysm. First-line treatment of tangle of vessels is also clogging with closed technique. In certain cases that this treatment is not suitable, surgeons remove the vessel tangle using microsurgical technique with open surgery. When the cause of the bleeding cannot be identified, depending on the size of bleeding, medical treatment is preferred for the absorption of the blood before surgical intervention. However, in large bleedings patients are taken into urgent operation to empty the blood due to sudden risk of death.
Signs and symptoms of brain hemorrhages…Patients usually present with sudden-onset severe headache, followed by sudden loss of consciousness and fainting. Projectile vomiting and seizures are frequently observed.
What needs to be done…. Brain hemorrhage is a life-threatening emergency situation, so the first thing to do is to call for professional help. Only 20% of patients having a brain hemorrhage can reach to a hospital; the rest pass away on the spot. The patient will be unconscious and therefore unable to do anything on his/her own. The patient should be lied flat, not moved, turned to his/her side when vomiting and airway should be kept open in case of seizures until health teams arrive.